The internet has evolved significantly since its inception, and now we stand at the cusp of a new era with the emergence of Web 3.0. In this blog post, we will explore the concept of Web 3.0 and its core components, such as decentralized web applications and tokenized networks. We will also discuss the distinguishing features of Web 3.0 compared to the traditional web, highlighting the transformative potential of blockchain technology.

A. What Is Web 3.0?
1. A Web 3.0 Introduction
Web 3.0 is considered the third generation of the internet, seen as an intelligent decentralized internet network consisting of multiple interconnected decentralized webs.
It is an internet where users not only have the freedom to access information but also can fulfill their needs quickly and conveniently without having to access multiple websites.
Web 3.0 will not build and deploy centralized applications on a single server or database as before. Instead, it will run on a blockchain network, a decentralized network of peer-to-peer nodes or a combination of both, to create an economic protocol integrated with cryptocurrencies. These applications are called decentralized applications and will be prevalent in Web 3.0.
2. Decentralized Web Apps
Blockchain seems to be the driving force of the next generation of the internet. Blockchain revolutionizes the way data is stored and managed by providing a shared and collectively managed data set. This unique state layer allows us to send data in a way that is protected by copies, enabling true peer-to-peer transactions without intermediaries. The platform for websites operated under this model is called the decentralized Web 3.0 platform.
Decentralized web applications, often referred to as dApps, are a fundamental component of Web 3.0. These applications are built on decentralized networks, such as blockchain, that distribute data and computational processes across multiple nodes rather than relying on a central authority. Unlike traditional web applications, dApps operate in a peer-to-peer manner, where interactions occur directly between users without intermediaries.
Blockchain technology plays a crucial role in enabling the decentralized and censorship-resistant nature of dApps. Blockchain is a distributed ledger that securely records transactions and data across a network of computers, ensuring transparency and immutability. By utilizing blockchain, dApps can leverage the decentralized consensus mechanism, allowing for trustless interactions and eliminating the need for third-party intermediaries. This decentralized architecture empowers users by giving them control over their data and reducing reliance on centralized authorities.
There are several benefits associated with using dApps – a key component of Web 3.0, enabled by blockchain technology. These applications offer increased privacy, data ownership, improved user experience, and enhanced security. By leveraging decentralized networks, dApps empower users and promote a more open and inclusive digital ecosystem.
3. Tokenized Networks
A decentralized network always requires a form of a decentralized cryptocurrency for members to exchange value. Tokenized is a decentralized economic system designed for the new generation of the internet.
The main difference between Tokenized Network compared and a conventional payment network is ensuring that transaction details are protected throughout the transaction lifecycle on the blockchain. We can understand that if Web 3.0 does not have a Tokenized Network, it is similar to Blockchain without Bitcoin. In that case, it would not be possible to run nodes to maintain the blockchain.
Tokenization has the potential to disrupt traditional business models and create new opportunities for value exchange by leveraging blockchain technology by introducing liquidity, enabling crowdfunding, transforming loyalty programs, and enhancing supply chain management. By leveraging blockchain technology, businesses can unlock new value exchange opportunities, empower stakeholders, and foster innovation in various sectors. As the tokenization ecosystem matures, we can expect to see further advancements and widespread adoption, leading to a more inclusive and efficient global economy.

B. What Are The Differences?
1. Basic Fundamentals
Function/Web Type | Traditional Web | Web 3.0 |
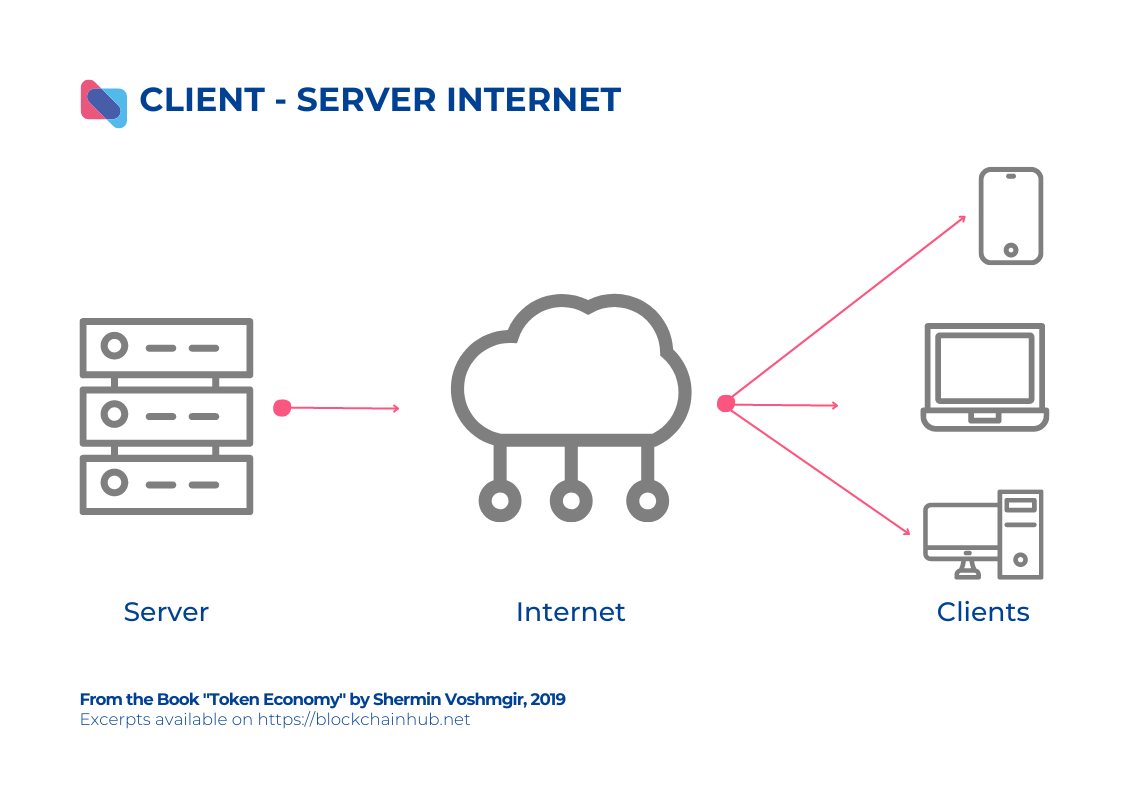
Operation Mode | Based on a centralized mechanism, meaning that data is managed on centralized servers and is prone to collapse. | Based on a decentralized mechanism, meaning that there will be no single server managing all nodes. Instead, nodes in the network will act as servers and communicate directly with each other, making it almost impossible to collapse or alter information on the Web 3 network. |
Required Standard | Traditional websites, due to their centralized nature, require a database management system to store data. | Since they operate based on a decentralized data mechanism, data will be stored on a distributed data network called IPFS (InterPlanetary File System) – every computer participating in the IPFS network can download and upload data without going through a server. In addition, application functions/data operations will be specified in Smart Contracts and permanently stored on the blockchain. |

2. Architecture and Data Ownership
In the traditional web, the architecture is predominantly centralized. Centralized architectures rely on a central authority or intermediary to control and manage data. This centralized control introduces vulnerabilities, as data is stored and controlled by a single entity, making it susceptible to breaches, manipulation, and censorship.
In contrast, Web 3.0 embraces a decentralized architecture. Decentralization is achieved through technologies like blockchain, which distribute data across a network of computers, eliminating the need for a central authority. This distributed architecture enhances security, resilience, and censorship resistance.
Web 3.0 places a strong emphasis on user ownership and control of data. With centralized systems, users often relinquish control of their data to platforms and service providers. Web 3.0 aims to empower users by enabling them to have ownership and control over their personal data. This shift allows individuals to determine how their data is accessed, shared, and monetized.
Distributed ledger technologies, such as blockchain, play a significant role in enhancing data privacy and protection in Web 3.0. Blockchain provides a transparent and immutable record of data transactions, ensuring that data cannot be altered or tampered with without consensus from the network participants. This increased transparency and security can help protect against data breaches, unauthorized access, and manipulation of sensitive information.
3. Interoperability and Seamless Experience
Interoperability refers to the ability of different systems, platforms, and applications to seamlessly interact and exchange data. Web 3.0 promotes interoperability by utilizing standardized protocols, open APIs, and decentralized technologies. This allows for the seamless integration of various services and applications across different platforms, creating a connected ecosystem.
The traditional web often suffers from data silos and walled gardens, where data is locked within specific platforms or services. This creates barriers and limits the flow of information and functionality between different systems. Web 3.0 aims to overcome these challenges by fostering open standards and protocols that facilitate data sharing and interoperability. By breaking down data silos, Web 3.0 enables a more inclusive and interconnected digital environment.
Through interoperability, Web 3.0 has the potential to deliver enhanced user experiences. Users can enjoy a seamless flow of data and services across multiple platforms and applications. For example, decentralized finance (DeFi) platforms can interact with decentralized identity systems, enabling streamlined and secure financial transactions. Interconnected applications can leverage shared data to provide personalized and context-aware services, creating a more tailored and convenient user experience.
4. Trust and Security
Web 3.0 utilizes blockchain technology to establish trust and enhance security. Blockchain operates on a decentralized network of computers, where transactions are recorded in a transparent and immutable manner. This distributed consensus mechanism eliminates the need for a centralized authority to validate and secure transactions, increasing trust in the system.
The immutability and transparency of blockchain contribute to enhanced security. Once data is recorded on the blockchain, it becomes nearly impossible to alter or delete without consensus from the network participants. This reduces the risk of fraud, tampering, and unauthorized changes to data. The transparent nature of blockchain also allows for public scrutiny and auditability, promoting accountability and trust.
Web 3.0 presents opportunities for secure identity management and authentication. With decentralized identity systems, individuals can have greater control over their digital identities, reducing reliance on centralized identity providers. Blockchain-based identity solutions offer enhanced privacy, as users can selectively disclose their identity attributes without revealing unnecessary personal information. This improves security by minimizing the risk of identity theft and unauthorized access to sensitive data.
Overall, Web 3.0’s utilization of decentralized architectures, emphasis on data ownership, interoperability, and blockchain-based trust and security mechanisms have the potential to reshape the digital landscape, offering increased privacy, seamless experiences, and enhanced trust for users.
Web 3.0 represents a paradigm shift in the way we interact with the internet, offering a decentralized, user-centric, and secure environment. Through decentralized web applications and tokenized networks, Web 3.0 leverages blockchain technology to redefine the traditional web. As we continue to embrace the transformative potential of Web 3.0, it is crucial to stay informed about the latest developments and opportunities it brings. With its enhanced privacy, data ownership, and seamless experiences, Web 3.0 holds the key to a more empowered and inclusive digital future.
We invite you to reach out to our outsourcing technology firm for consultation and assistance in implementing blockchain solutions. Together, let’s unleash the power of blockchain and shape a future of secure and transparent industries.
Claim Your Best Service Ever:
SparkMinds - We Are More Than Your Demand And Satisfaction!
SparkMinds Joint Stock Company - An Outsourcing Technology Firm
info@demo.sparkminds.net
Floor 3, Moc Gia Building (M.G), 24A Bau Cat 2 Street, Ward 14, Tan Binh District, Ho Chi Minh City, Vietnam