Discover the compelling reasons for your business to initiate the development of a cloud infrastructure setup promptly by delving into this blog post!
1. Understand the Cloud Infrastructure
A. What's That
Cloud infrastructure refers to the collection of hardware and software components that enable the delivery of cloud computing services over the internet.
It provides organizations with access to a virtualized environment where they can store, manage, and process data and applications without the need for physical infrastructure on-site. Cloud infrastructure is made up of servers, storage devices, networking components, virtualization software, and management tools, all hosted and maintained by cloud service providers.
B. Advantages
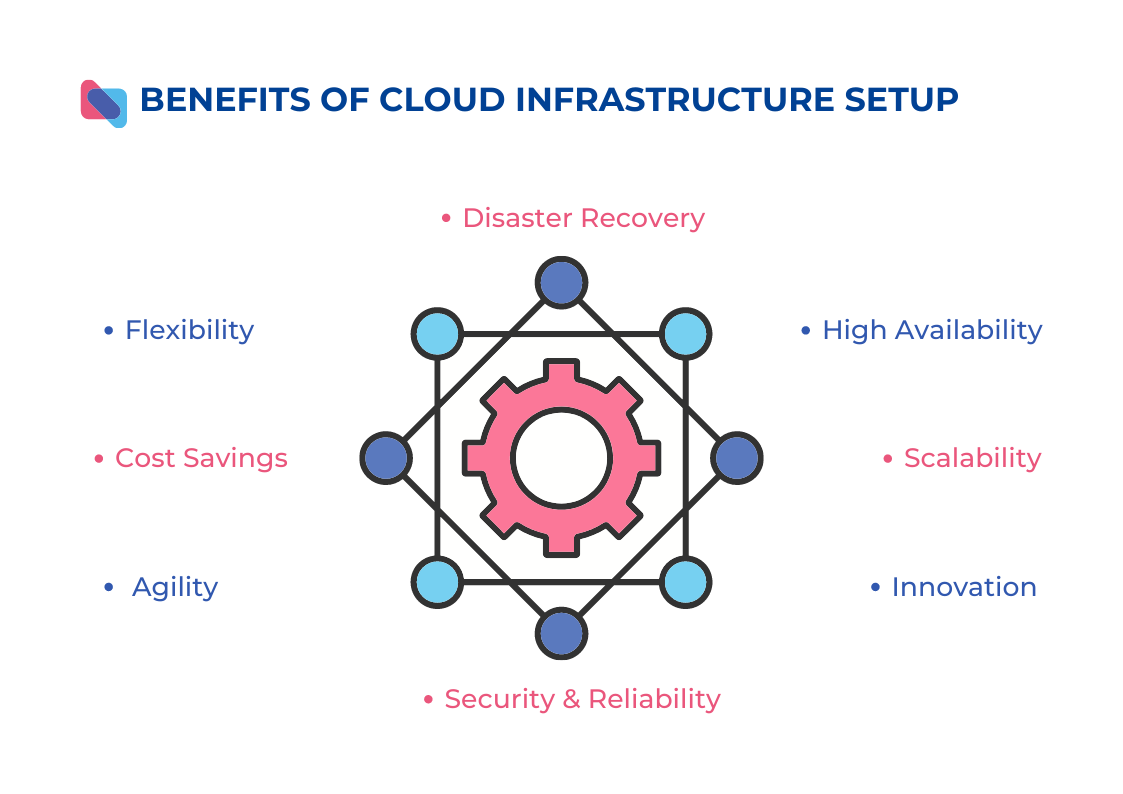
The significance of cloud infrastructure in modern businesses is immense. Here are some key aspects:
- Scalability: Cloud infrastructure offers organizations the ability to scale their resources up or down quickly and easily based on their needs. This scalability eliminates the need for upfront investments in hardware and allows organizations to pay only for the resources they actually use, resulting in cost savings and improved operational efficiency.
- Flexibility: With cloud infrastructure, businesses can access their data and applications from anywhere with an internet connection. This flexibility enables remote work, collaboration among teams in different locations, and easy access to critical resources for employees, partners, and customers. Additionally, organizations can choose from a variety of cloud deployment models, including public, private, and hybrid clouds, to meet their specific requirements and regulatory compliance needs.
- Cost Savings: Cloud infrastructure eliminates the need for organizations to maintain and upgrade their own physical infrastructure, reducing upfront capital expenditures. This cost-effective approach allows businesses to allocate their IT budgets more efficiently and invest in other strategic initiatives.
- Reliability and Disaster Recovery: Cloud service providers typically offer robust infrastructure with high availability and redundancy measures. Cloud infrastructure also facilitates easy backup and recovery processes, enabling businesses to quickly restore operations in the event of an unforeseen incident.
- Innovation and Agility: With cloud infrastructure, businesses can leverage a wide range of development tools, platforms, and services provided by the cloud service providers. This enables faster application development and deployment cycles, promoting innovation and agility. Organizations can experiment, iterate, and scale their applications more rapidly, gaining a competitive edge in the market.
C. Types of Cloud Services
Among the various cloud service models, Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS), Platform as a Service (PaaS), and Software as a Service (SaaS) stand out as key options.
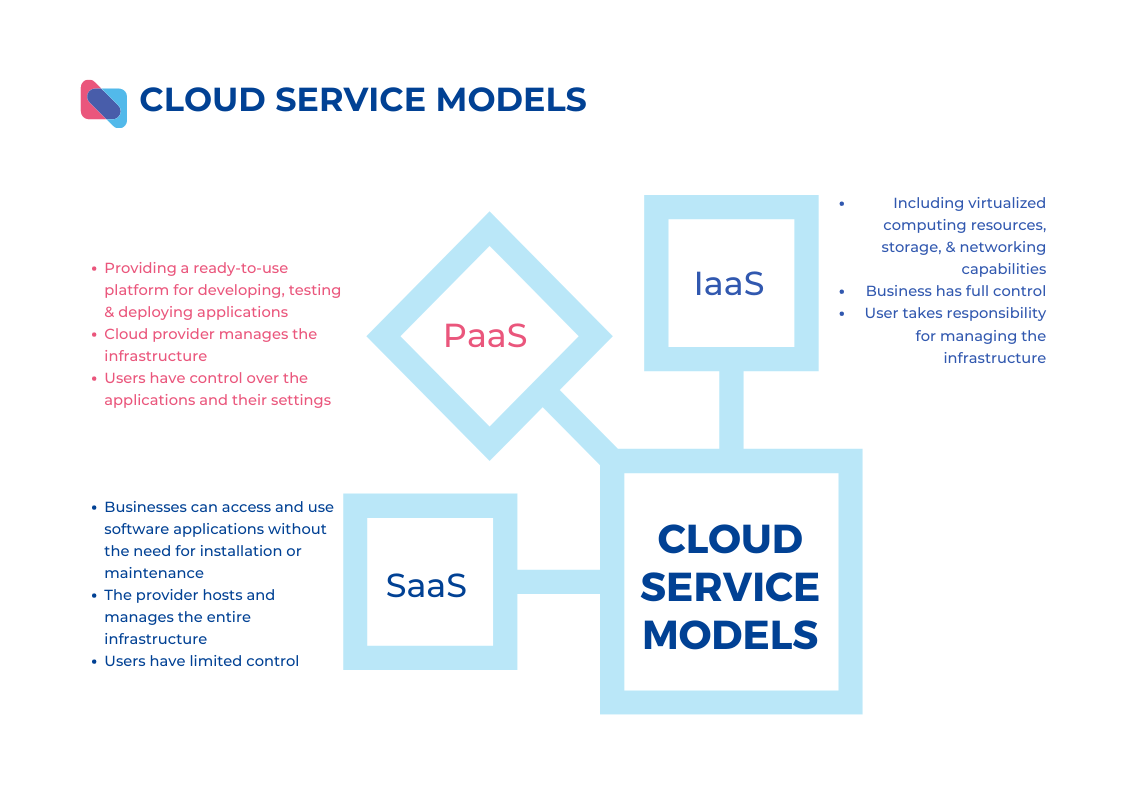
- Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS): IaaS provides the fundamental building blocks of IT infrastructure, including virtualized computing resources, storage, and networking capabilities. With IaaS, businesses have full control over their infrastructure and can manage and configure it according to their specific requirements. This level of control allows organizations to install and run their own operating systems, applications, and development frameworks. However, the responsibility for managing the infrastructure, including security, maintenance, and updates, falls on the user.
- Platform as a Service (PaaS): PaaS offers a higher level of abstraction by providing a ready-to-use platform for developing, testing, and deploying applications. With PaaS, businesses can focus on application development without worrying about the underlying infrastructure. The cloud provider manages the infrastructure, including servers, storage, and networking, while offering a set of tools, frameworks, and services for application development. Users have control over the applications and their settings, while the provider takes care of the underlying platform and infrastructure management.
- Software as a Service (SaaS): SaaS is the most user-friendly cloud service model, where applications are delivered over the internet as a complete service. With SaaS, businesses can access and use software applications without the need for installation or maintenance. The provider hosts and manages the entire infrastructure, platform, and software application, including updates and security patches. Users have limited control over the application’s settings and configuration, primarily focusing on using the software to meet their needs.
2. Popular Cloud Provider
A. About AWS
Amazon Web Services (AWS) is a leading cloud service provider, offering a comprehensive suite of cloud computing services. With its vast range of offerings, AWS has gained a significant market share and become a go-to choice for organizations seeking reliable and scalable cloud solutions.
- Market Share
- Core Offerings
- Compute Services
- Storage Services
- Database Services
- Networking Services
- Developer Tools
B. Key Features
AWS stands out for its notable features that enhance performance, scalability, and reliability:
- Scalability: Allows businesses to scale their resources up or down based on demand, ensuring optimal performance and cost efficiency.
- High Availability: Designed for high availability, providing redundancy and fault-tolerant systems to minimize downtime.
- Security: Offers robust security measures, including encryption, access controls, and compliance certifications, to protect data and meet regulatory requirements.
- Global Infrastructure: Has a vast global network of data centers, enabling businesses to deploy their applications and services in multiple regions.
- Cost Optimization: Provides various pricing models, cost management tools, and resource optimization options to help businesses optimize their cloud spend.
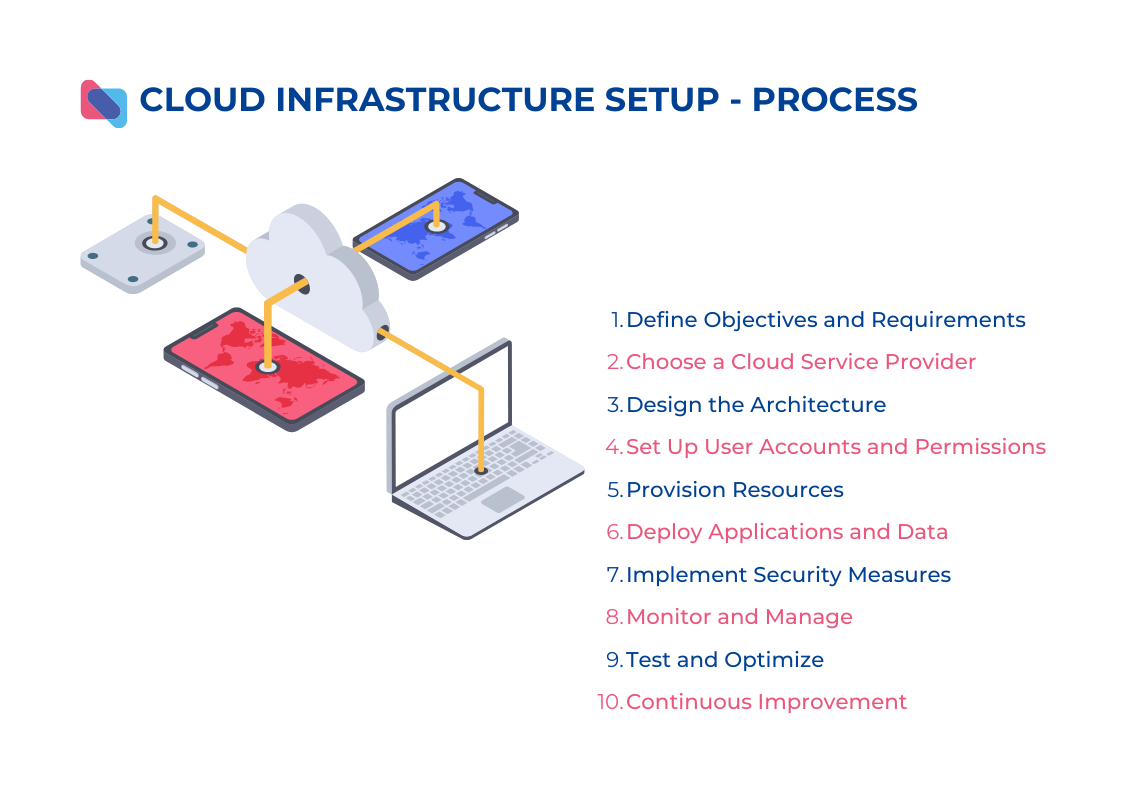
3. A Cloud Infrastructure Setup Process
The process of setting up a cloud infrastructure typically involves several steps. While the specific details may vary depending on the cloud service provider and the organization’s requirements, the following outlines a general framework for setting up a cloud infrastructure:
- Define Objectives and Requirements: The first step is to clearly define the objectives and requirements of the cloud infrastructure. This includes understanding the organization’s needs, such as scalability, reliability, security, and cost-effectiveness.
- Choose a Cloud Service Provider: Select a cloud service provider that aligns with the organization’s requirements and objectives.
- Design Architecture: Based on the requirements, design cloud infrastructure architecture. This involves determining the appropriate cloud services and components to be used, such as virtual machines, storage options, networking configurations, and security measures. Consider factors like scalability, high availability, data backup, disaster recovery, and network connectivity.
- Set Up User Accounts and Permissions: Create user accounts and define appropriate permissions and access controls for different individuals or teams within the organization.
- Provision Resources: This may include creating virtual machines, storage volumes, databases, load balancers, and other infrastructure components.
- Deploy Applications and Data: Migrate or deploy the organization’s applications, data, and workloads to the cloud infrastructure. This may involve installing and configuring software, setting up databases, transferring data to cloud storage, and ensuring proper integration with other services or systems.
- Implement Security Measures: Implement robust security measures to protect the cloud infrastructure and data. This includes configuring firewalls, enabling encryption for data in transit and at rest, setting up intrusion detection and prevention systems (IDPS), and regularly patching and updating software and systems.
- Monitor and Manage: Implement monitoring and management tools to track the performance, availability, and usage of the cloud infrastructure. Set up alerts and notifications for potential issues or resource utilization anomalies. Establish processes for managing backups, scaling resources, and conducting routine maintenance tasks.
- Test and Optimize: Conduct thorough testing of the cloud infrastructure and applications to ensure they function as expected. Optimize the infrastructure for performance, cost, and efficiency by fine-tuning configurations, rightsizing resources, and implementing auto-scaling mechanisms.
- Continuous Improvement: Cloud infrastructure is an ongoing process, and it requires continuous improvement and optimization. Regularly assess the performance, security, and cost-effectiveness of the infrastructure, and make adjustments as needed to meet evolving business needs.
4. Future Trends
Emerging trends in cloud infrastructure setup indicate that cloud technology is continuously evolving to meet the changing needs of organizations. Here are three significant trends that have gained momentum in recent years:
- Serverless Computing
- Containerization
- Hybrid Cloud Environments
Looking ahead, several trends are likely to shape the future of cloud infrastructure setup:
- Edge Computing
- Multi-Cloud Strategies
- AI and Machine Learning Integration
As technology advances, organizations can expect further developments in areas like edge computing, multi-cloud strategies, and AI/ML integration. Staying updated with these trends will help organizations optimize their cloud infrastructure and unlock the full potential of cloud technology for their business needs.
Remember, our team of experienced developers is here to guide you every step of the way.
Contact us today to embark on your development journey and unlock a world of endless possibilities.
Claim Your Best Service Ever:
SparkMinds - We Are More Than Your Demand And Satisfaction!
SparkMinds Joint Stock Company - An Outsourcing Technology Firm
info@demo.sparkminds.net
Floor 3, Moc Gia Building (M.G), 24A Bau Cat 2 Street, Ward 14, Tan Binh District, Ho Chi Minh City, Vietnam